
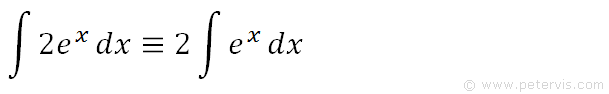
The first form of Green’s theorem that we examine is the circulation form. In particular, Green’s theorem connects a double integral over region D to a line integral around the boundary of D. Green’s theorem also says we can calculate a line integral over a simple closed curve C based solely on information about the region that C encloses. Green’s theorem says that we can calculate a double integral over region D based solely on information about the boundary of D. Green’s theorem takes this idea and extends it to calculating double integrals. From this, we have, dx = du/2.Figure 6.32 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus says that the integral over line segment depends only on the values of the antiderivative at the endpoints of. To find the integral ∫ e 2x+1 dx, assume that 2x+1 = u. Since we usually add an integration constant C for every indefinite integral, The integral and d/dx get canceled with each other on the left. We know that the derivative of e 2x is 2e 2x. How to Find the Integral of e to the 2x by Differentiation?

No, the derivative of e 2x is 2e 2x whereas the integral of e 2x is e 2x/2 + C. Is the Derivative of Integral of e to the 2x the Same? Then the value of the integral is, (1/2) ∫ e u dx = (1/2) e u + C = (1/2) e 2x + C.
To find the ∫ e 2x dx, assume that 2x = u. How to Find the Integral of e to the power of 2x? We can write this mathematically using the integration symbol as ∫ e 2x dx = e 2x/2 + C.

Extending this further, the integral of e ax +b is e ax+b/a + C.įAQs on Integral of e to the 2x What is the Value of the Integral of e to the 2x?.Hence, the integral of e ax, in general, is e ax/a + C.The integral of e to the 2x is e 2x/2 + C, where C is the integration constant.Important Notes on Integral of e to the 2x: Thus, the integration constant doesn't play any role while calculating the definite integral (because it got canceled). To evaluate this, we will first consider the fact that the integral of e 2x is e 2x/2 + C and then substitute the upper bound and lower bound one after the other in order and then subtract the results. We will consider the definite integral of e to the 2x from a to b. A definite integral is an integral with the bounds (lower and upper bounds).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
